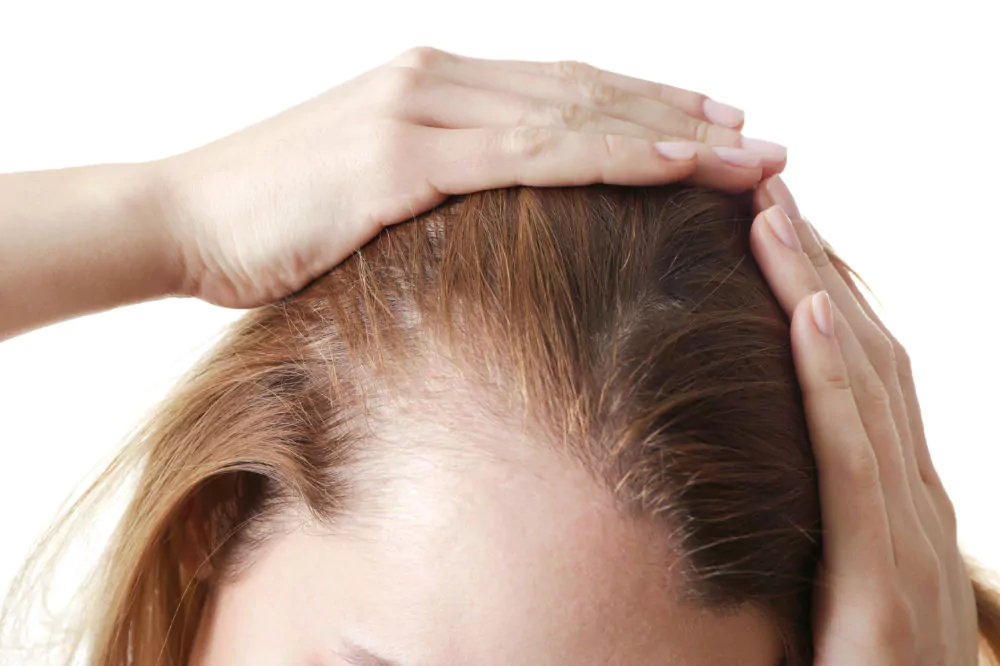
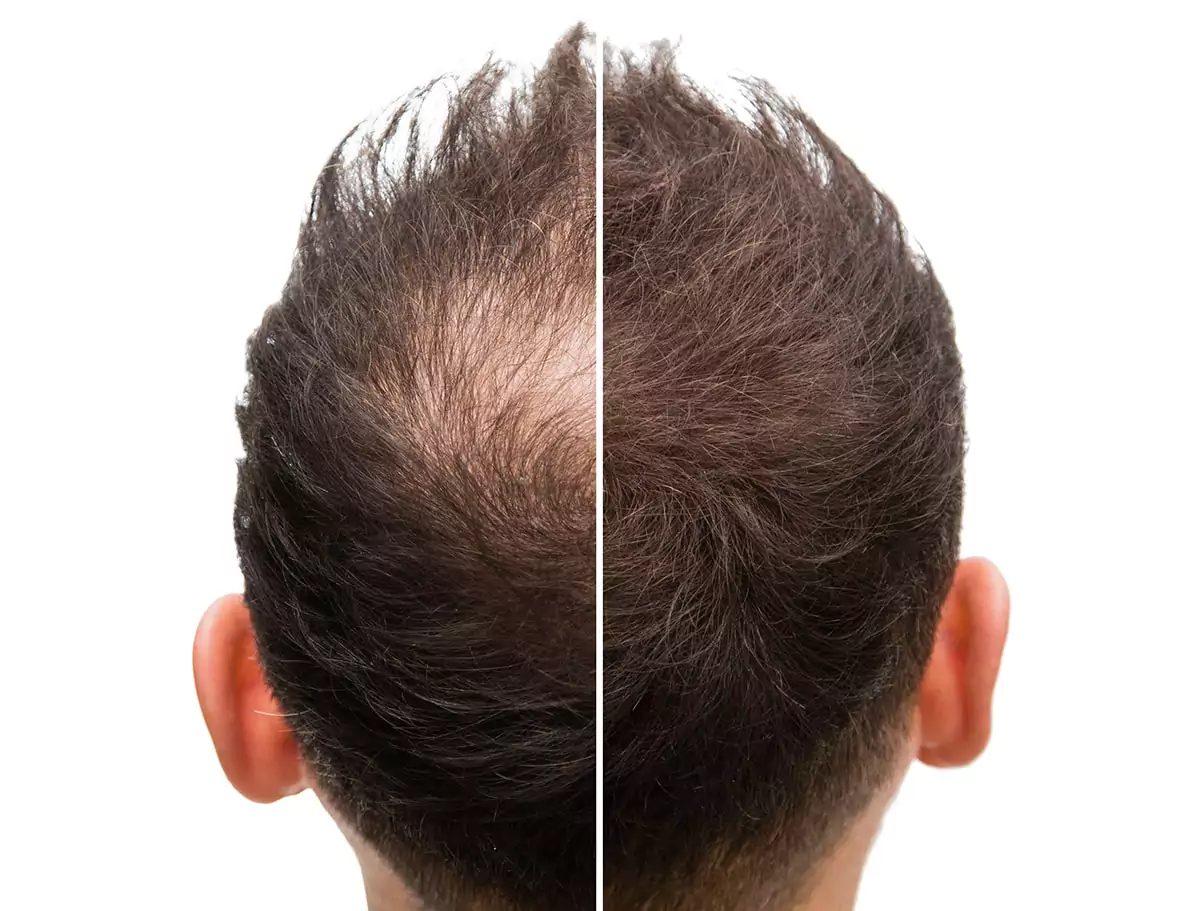
Have you grown alarmed at the amount of hair you’ve been finding in your shower drain? Or maybe you’ve noticed that your hairline is retreating or the part in your hair is widening? Whether you’ve recently begun experiencing hair loss and thinning or you’ve always had fine hair texture, you’re probably wondering how to get thicker hair.
By age 50, nearly 75% of men and 40% of women experience hair thinning and loss. Heredity, hormones, stress, diet, health issues, ageing, and hairstyling can prevent healthy hair growth, causing it to thin and fall out. Hair thinning and loss can result in anxiety, depression, and reduced self-esteem.
Fortunately, over-the-counter and medical treatments are available to restore hair health and create fuller hair. At Hair and Skin Science, we use a revolutionary medical therapy called platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to help men and women get thicker hair and restore hair growth. Let’s explore what causes thin hair and different ways to thicken it.
What Causes Hair Loss and Thinning: Male vs. Female

Anyone can experience hair thinning, but it’s most common in men and women over 30. Many factors contribute to hair thinning and loss (also called alopecia). Depending on the cause, hair issues can occur suddenly or gradually.
The most common cause of hair thinning is androgenetic alopecia, which affects both men and women. This hereditary condition—also known as male or female pattern balding—accounts for almost 95% of hair thinning in men. While androgenetic alopecia is responsible for most male hair loss and female hair loss, it impacts the sexes differently.
Almost all men experience some level of male pattern balding. The condition, which causes a receding hairline and thinning hair on the scalp’s crown, is associated with the male hormone testosterone. The hormone causes hair follicles to shrink, which first thins the hair strands that the follicle produces and then stops production completely.
Female pattern balding is also caused by testosterone, but because women don’t have as much testosterone as men, androgenetic alopecia affects women differently. The condition causes less extreme hair thinning in women, who typically start experiencing thinning along their hair’s part line. Women with female pattern balding rarely lose all or most of their hair.
Some other causes of hair thinning include:
- Alopecia areata: A medical condition in which your body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, causing them to stop producing hair strands. Alopecia areata affects about 2% of people worldwide.
- Traction alopecia: This condition, which affects women more than men, is caused by pulling on your hair repeatedly. Risk factors include wearing your hair in a tight bun or braids, using hair extensions, wearing rollers, and using heat and chemicals on your hair. The condition is reversible but can result in permanent loss without behavioural changes.
- Telogen effluvium: A common condition brought on by stress or shock, telogen effluvium causes temporary hair thinning and loss. Pregnancy, poor diet, sudden weight loss, and emotional and physical stress can temporarily impact hair growth.
- Nutritional deficiencies and medication: Low levels of iron, protein, and vitamins E and D can lead to hair shedding. Some drugs, particularly birth control pills, can result in hair thinning.
Regardless of what’s causing you to lose your hair, there are many options available to make your existing hair look thicker and even regrow healthy hair.
Home Options

You don’t need a celebrity hairstylist to teach you how to get thicker hair. Here are a few suggestions on how to grow thicker, healthier hair at home:
- Change your diet: If you’re wondering how to get thicker hair through diet, eat foods rich in protein, fatty acids, vitamin A, vitamin D, and vitamin E.
- Use gentle styling products: Choose gentle shampoos and hair products that contain histidine, phyto-caffeine, niacin, biotin, and essential oils. Hairstyling products that contain castor oil, olive oil, and other oils also show promise in protecting thinning hair. Using olive oil or a castor oil hair supplement on your scalp can prevent dandruff, a cause of hair thinning.
- Loosen your hair: If you pull your hair tightly in the same direction repeatedly, the strain can permanently damage your hair follicles and strands. If you experience excessive scalp itching, sores, a receding hairline, or patches of thin hair, stop wearing braids, buns, ponytails, hair extensions, and weaves.
- Scalp massage: Some evidence suggests that regular scalp massages, which improve blood circulation to the scalp, can make hair thicker.
- Avoid harsh chemicals and treatments: Don’t use hair relaxers or other chemical treatments and products, including dry shampoo. Dry shampoo can interfere with hair follicles and cause hair to fall out.
Treatment Options
Scientists have made many hair growth advances in recent years. Here are a few effective medical treatment options for most hair types:
- Medication: Minoxidil is an over-the-counter drug that is available in a foam or shampoo. Finasteride is a prescription drug exclusively for men that’s available in pill form. Both have shown results in hair growth.
- Surgery: Hair transplant surgery (also called hair restoration) is a procedure that restores hair to areas of the scalp with bald or thinning hair. There are several types of transplant surgery, but most involve a surgeon harvesting hair strands or tissue from one area of the scalp and relocating it to a balding area.
- PRP: One of the newest treatments for hair thinning is platelet-rich plasma. PRP is a non-surgical therapy for hair thinning and loss. The treatment uses your blood platelets and scalp stimulation to strengthen your hair follicles and promote thicker hair growth.
Why PRP is a Great Choice

Doctors use PRP treatments to heal damage to muscles, joints, tendons, and skin. In recent years, physicians have used PRP to treat male and female pattern balding. At Hair and Skin Science, we use PRP to treat hair and skin conditions.
The PRP treatment is a three-step process:
- First, we collect blood from your arm and process it in a centrifuge to separate the platelets. These platelets are rich in growth factors which can assist in healing.
- We make small injections with the PRP into areas of the scalp where there is hair loss or hair thinning.
- We then carefully micro-needle the entire scalp which encourages blood flow and stimulates hair follicles. The process causes little discomfort.
PRP contains healing and growth agents that instruct cells to work at peak performance. Combining PRP with microneedling boosts blood supply to the scalp and follicles. The treatment helps:
- Activate natural hair growth
- Create thicker hair strands and make hair look fuller
- Extend the hair’s growth cycle
PRP treatment is safe and effective for people with androgenetic alopecia, as well as stress-related and genetic hair issues. It’s most effective in the early stages of hair thinning. You can combine PRP with medical treatments and over-the-counter products for a multi-pronged approach to hair thinning.
FAQs
How Many PRP Treatments Will I Need?
We recommend that patients start the PRP process by undergoing treatments every two to three weeks before lengthening the time between appointments. Regular treatments help keep hair follicles stimulated. On average, most people require about 10 treatments a year to ensure that they maintain hair growth.
How Long Do Treatments Take?
PRP treatments take between 30 and 45 minutes, depending on how big an area we are treating.
Is PRP Treatment Painful?
The PRP and microneedling process has minimal discomfort, depending on each individual. We use very fine needles.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
Most people start seeing a decrease in hair shedding soon after starting PRP therapy. Natural hair grows slowly—only about half an inch a month. You can expect to see hair sprouting several weeks after your first treatment, but it will take months before it grows to a noticeable length. Most people experience visible growth about three months into treatment and see full results within six to 12 months. Find more information by checking out before and after photos.
Is PRP Safe?
PRP is one of the safest hair treatments available with few side-effects. In rare cases, you might have soreness or bruising following a treatment. Find more health information on our PRP treatment page.
Who Does PRP Work Best On?
PRP is the best treatment for you if you are a man or woman with androgenetic alopecia or someone who is experiencing temporary hair loss from an illness, pregnancy, or stress. PRP works well on people who still have some hair and functioning follicles.
Is There a Recovery Period or Restrictions After Treatment?
You can return to normal activities immediately after treatment.
Where Can I Get PRP Treatments?
The medical team and Hair and Skin Science has over 30 years of experience in healthy hair regrowth. We have performed more than 45,000 PRP treatments throughout the London areas. If you’re wondering how to get thicker hair, book an appointment for a free consultation today and we’ll be able to assess your scalp to see if you’re a suitable candidate for our PRP hair loss treatments.